Understanding Peyronie’s Disease: A Comprehensive Overview:
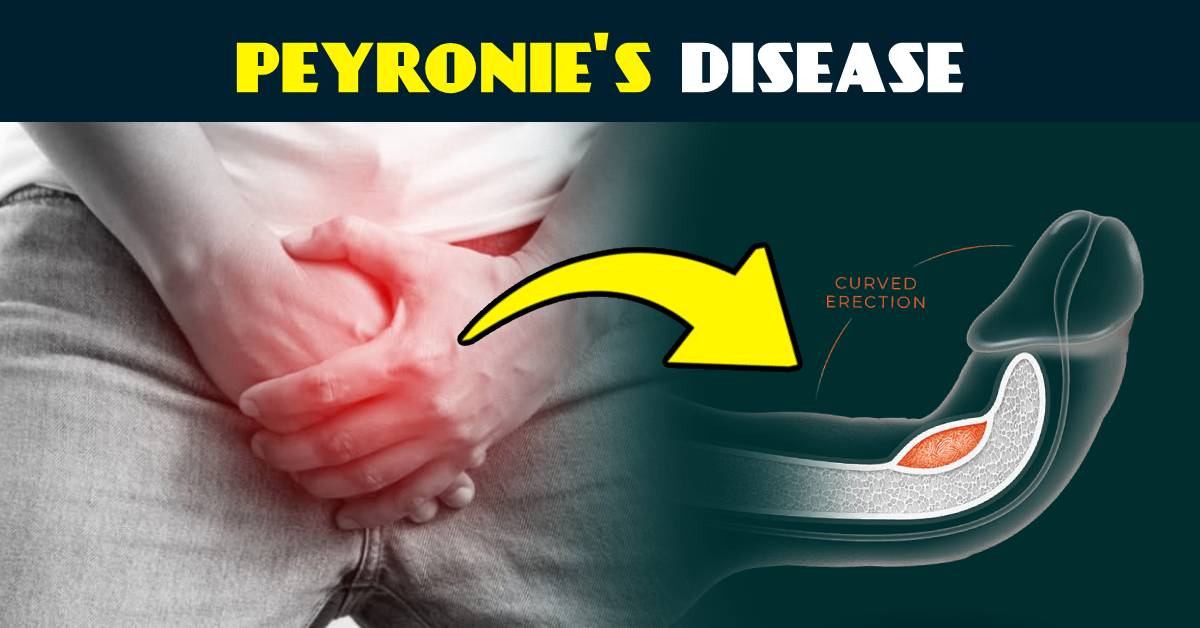
- Peyronie’s disease is a condition that affects the male sex organ, which can have negative emotional effects on individuals. It is characterized by the formation of stiff scar tissue within the penis, leading to curvature and pain during erections. In this blog, we will explore the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, available treatment options, and coping strategies related to Peyronie’s disease.
What is Peyronie’s Disease?
Peyronie’s disease is a disorder of connective tissue that causes the penis to bend or curve during an erection. This curvature often results in discomfort, pain, and difficulties with sexual intercourse. The condition is named after Claude Francois de la Peyronie, the French surgeon who first described it in the 18th century. Although it can occur at any age, it is more prevalent in men over 40 years old.
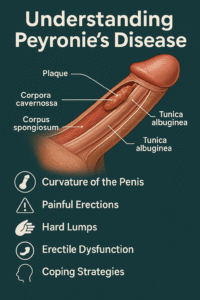
To better understand Peyronie’s disease, it is essential to know a little about the anatomy of the penis. The penis is composed of three main parts:
- Corpora Cavernosa: Two cylindrical structures that run along the length of the penis and fill with blood during an erection.
- Corpus Spongiosum: A single structure that surrounds the urethra and, like the corpora cavernosa, fills with blood to help keep the urethra open during an erection.
- Tunica Albuginea: A fibrous sheath that surrounds the corpora cavernosa and provides structural support.
In Peyronie’s disease, plaques form in the tunica albuginea, leading to the characteristic curvature.
Symptoms of Peyronie’s Disease
Symptoms of Peyronie’s disease can significantly vary among individuals. The most common symptoms include:
- Curvature of the Penis: This is the most obvious symptom, which may be upwards, downwards, or sideways at the time of erection.
- Pain: Many individuals experience pain or sensitivity during erections and possibly in the flaccid state.
- Changes in Size: Some men may notice a loss in length or girth of the penis.
- Lumps: Palpable hard lumps or plaques can be felt along the shaft of the penis.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Some men may develop problems getting or maintaining an erection.
Table 1: Common Symptoms of Peyronie’s Disease
| Symptom | Description |
| Curvature | The penis bends when erect |
| Pain | Painful erections or discomfort |
| Changes in Size | Shortening of the penis or decreased girth |
| Lumps | Hard knots along the penis shaft |
| Erectile Dysfunction | Problems with getting and/or maintaining an erection |
Causes of Peyronie’s Disease
The specific causes of Peyronie’s disease are not fully understood; however, several factors are thought to play a role in triggering the condition:
- Trauma or Injury: Any kind of physical injury to the penis, whether during sex, sports, or accidents, can lead to scar formation.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of Peyronie’s disease or other connective tissue disorders may increase susceptibility.
- Connective Tissue Disorders: Conditions such as Dupuytren’s contracture, which affects the hands, are linked with Peyronie’s disease.
- Age: The incidence of Peyronie’s disease increases with age, particularly in men over 40.
- Other Health Conditions: Conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and certain autoimmune diseases may also contribute to the development of Peyronie’s disease.
Table 2: Potential Causes of Peyronie’s Disease
| Cause | Description |
| Trauma or Injury | Physical damage to the penis |
| Genetic Factors | Family history of connective tissue disorders |
| Connective Tissue Disorders | Conditions affecting connective tissue |
| Age | Increased risk in men over 40 |
| Other Health Conditions | Diabetes, high blood pressure, autoimmune diseases |
Diagnosis of Peyronie’s Disease
Diagnosis typically involves taking a medical history and physically examining the patient. The doctor will assess the degree of curvature and inquire about the onset of symptoms. In some cases, imaging studies, such as ultrasound, may be used to determine the nature of the curvature and verify the presence of plaques.
Diagnostic Tests
- Physical Examination: The physician will inspect the penis for any deformity, masses, or curvature.
- Ultrasound: This imaging test can help visualize the plaques and assess blood flow to the penis.
- Penile Angiography: In rare cases, this test may be performed to evaluate blood vessels in the penis.
Treatment Options for Peyronie’s Disease
The treatment of Peyronie’s disease depends on the severity of the condition, the degree of curvature, and the symptoms experienced. Options include:
- Medications
While there are no FDA-approved oral medications specifically for Peyronie’s disease, some may help alleviate symptoms:
- Pentoxifylline: Enhances blood flow and may decrease the size of plaques.
- Vitamin E: Some studies suggest it may reduce curvature, although results are mixed.
- Injections
- Collagenase Clostridium Histolyticum (Xiaflex): An FDA-approved injectable treatment that effectively degrades the scar tissue to reduce curvature and improve functionality.
- Devices
- Vacuum Erection Devices: These create a vacuum around the penis, enhancing blood flow and may help in straightening the penis over time.
- Surgery
For cases unresponsive to other treatments or those with severe curvature, surgery may be an option:
- Plication Surgery: This involves stitching the opposite side of the curvature to straighten the penis.
- Grafting: In severe cases, grafting may be performed to replace the scar tissue with healthy tissue.
Table 3: Treatment Options for Peyronie’s Disease
| Treatment Type | Description |
| Medications | Oral or injectable treatments to reduce symptoms |
| Vacuum Devices | Devices to improve blood flow and curvature |
| Surgery | Options include plication or grafting |
Coping with Peyronie’s Disease
Living with Peyronie’s disease can be a psychological burden. It is essential for patients to communicate openly with their partners and utilize healthcare providers as resources. Coping strategies include:
- Communication: Discussing the problem with a partner can reduce anxiety and foster understanding.
- Counseling: Seeking psychological therapy can help address emotional distress related to the condition.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide a sense of community and allow individuals to share experiences with others.

Conclusion
Peyronie’s disease can complicate a man’s quality of life. Effective management of the condition requires an understanding of its symptoms, causes, and available treatment options. If you suspect you have Peyronie’s disease, seek professional healthcare for proper diagnosis and treatment. Remember, you are not alone, and there are resources available to help you navigate this condition.